| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
- 책
- docker
- DBMS
- 자바
- Python
- 명령어
- spring
- mysql
- 오블완
- PostgreSQL
- SQL
- oracle
- 인터페이스
- 티스토리챌린지
- mssql
- 인덱스
- java
- 후기
- github
- Javascript
- 네트워크
- Linux
- MariaDB
- error
- git
- 독서
- springboot
- 리눅스
- IntelliJ
- pandas
- Today
- Total
hanker
Spring Boot - 메서드 호출 전/후 로깅 (AOP) 본문
프로젝트에서 주로 사용되는 AOP 로깅 기능에 대해서 알아보자
프로젝트 내에서 각 메서드가 실행 전과 실행 후 그리고 정상 적으로 return 되었을 경우와 예외 발생 했을 때 로그를 찍어보자.
사용되는 어노테이션은 아래와 같다.
@Aspect
- @Before : 메서드 실행 전
- @After : 메서드 실행 후
- @AfterReturning : 메서드 실행 후 결과값
- @AfterThrowing : 메서드 실행 후 예외값
@Aspect
@Component
public class loggingAop {
// 메서드 실행 전 로깅
@Before("execution(* com.hanker.exampleboot.api.controller.*.*(..))")
public void logBeforeMethodExecution(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("@Before 실행 method: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName() +
", 인수: " + java.util.Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
// 메서드 실행 후 로깅
@After("execution(* com.hanker.exampleboot.api.controller.*.*(..))")
public void logAfterMethodExecution(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("@After 실행완료: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
// 메서드가 정상적으로 리턴된 후 결과 로깅
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "execution(* com.hanker.exampleboot.api.controller.*.*(..))", returning = "result")
public void logAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
System.out.println("@AfterReturning 실행 method : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName() + ", return 값: " + result);
}
// 메서드에서 예외 발생 시 로깅
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "execution(* com.hanker.exampleboot.api.controller.*.*(..))", throwing = "error")
public void logAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable error) {
System.out.println("@AfterThrowing 오류 method: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName() +
" 오류 message: " + error.getMessage());
}
}어노테이션 내 표현식을 설명하자면,
* com.hanker.exampleboot.api.controller.*.*(..)* : 반환타입 지정 ( *를 사용하면 모든 반환 타입을 지정할 수 있다)
com.hanker.exampleboot.api.controller.*.*(..) : 패키지 및 클래스 명.메서드명(파라미터)
@RestController
public class TRestController {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
public TRestController(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
@RequestMapping("/t/v1/getData")
public User getData(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params, Model model) {
Optional<User> userMap = userRepository.findByUserId(params.get("userId").toString());
return userMap.get();
}
@RequestMapping("/t/v1/setData")
public User setData(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params) {
User user = new User();
return userRepository.save(user);
}
}
데이터를 불러오고 저장하는 테스트 케이스를 만들었다.
해당 부분은 그냥 로깅 테스트를 위함이고, 위 코드를 사용하려면 추가적으로 설정이 필요하다.
실행 후 URL 호출을 해보자.
http://localhost:8080/t/v1/getData?userId=admin

실행 결과를 보면 @Before 어노테이션을 지정한 부분이 제일 먼저 호출되었고, 그 다음 @AfterReturning 어노테이션, @After 가 실행되었다.
순서는 메서드 실행전 > 메서드 결과값 > 메서드 종료
이제 예외를 발생시켜서 확인해보자
파라미터로 userId값을 받아야 하는데 없애고 보내보자
http://localhost:8080/t/v1/getData
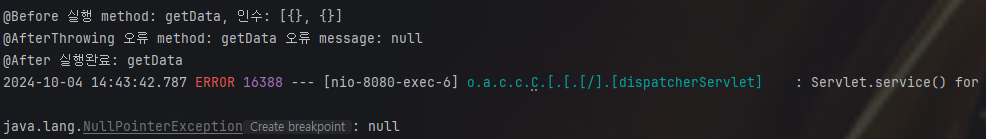
실행 결과를 보면 @Before 어노테이션을 지정한 부분이 제일 먼저 호출되었고, 그 다음 @AfterReturning어노테이션, @After 가 실행되었다.
순서는 메서드 실행전 > 메서드 예외 발생값 > 메서드 종료
이런 방식으로 AOP를 활용해서 특정 서비스를 모니터링 할 수 있고, 메서드에 하나씩 설정해서 사용해야하는 부분들을 간편하게 Spring에서 지원해주니 너무 편하다.
이 글에서는 간단하게 어떻게 실행되는지에 대해서 적어봤는데, 응용할 수 있는 부분들이 너무 많다.
끝.
'SPRING' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring boot - application.properties Oracle DB 설정 (properties/yml) (0) | 2024.10.10 |
|---|---|
| Spring - excel to csv 파일 변환 (한글 깨짐 문제 완벽 해결) (0) | 2024.10.06 |
| Spring boot - application.properties MSSQL DB 설정 (2) | 2024.09.29 |
| Spring Boot - 스케쥴러 설정 방법 (0) | 2024.09.08 |
| javax.persistence.TransactionRequiredException: Executing an update/delete query (0) | 2024.09.04 |




